COVID-19 Will Not Make Income Inequality Worse
Let’s assume that we beat COVID-19 over the next month or two and then reopen the economy. What happens next? Some economists believe the shock of the pandemic will produce a traditional recession and a traditional long recovery. Others think we can bounce back pretty quickly. I happen to be in the latter camp, but either way it’s worth pushing back on stuff like this:
“There will likely be some permanent damage inflicted on the economy,” says Greg Daco, chief US economist at Oxford Economics. “What this shock is doing is exacerbating preexisting inequality issues across the country. The individuals who have been hit the hardest are the individuals who were in the most precarious position to start with.”
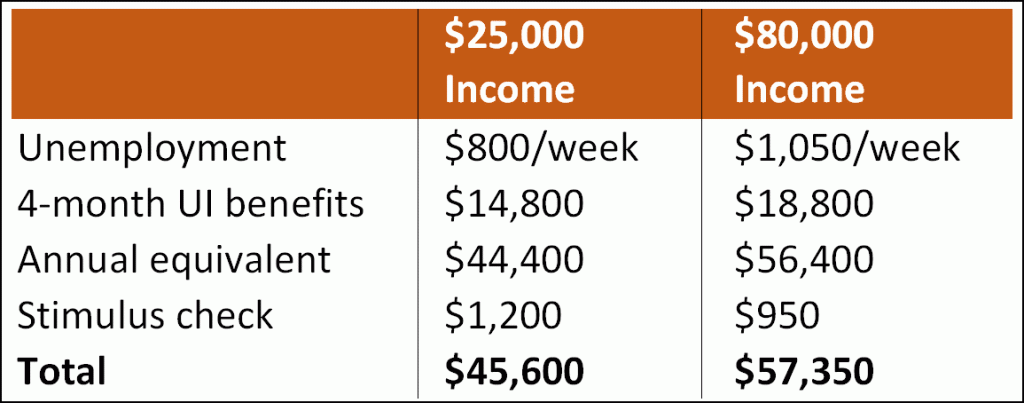
This is just not true. The coronavirus rescue bill is immensely progressive, providing far more money to the poor than to the rich. Here’s a rough calculation of benefits at both ends of the income spectrum:
For the four months she’s out of work, a low-income worker would see her annualized income rise from $25,000 to $45,600. The high-income worker would see her annualized income drop from $80,000 to $57,350. This is due mostly to the flat $600 unemployment bonus that everyone gets regardless of previous income.
Whatever else you can say about this, it reduces income inequality. For a few months, anyway.
This doesn’t mean there are no low-income workers who will suffer economically from the COVID-19 pandemic. Of course there will be. But for the vast majority, their income will either stay the same (if they remain employed) or increase considerably (if they lose their jobs). This is one of the reasons I think we’ll be able to bounce back from our artificial recession fairly quickly.