Here’s How Globalization Has Affected America
How much has globalization hurt the American worker? Entire forests have been felled around this question, but here’s a simple way of getting a rough read on things.
Globalization mainly affects what’s called the tradeable sector—that is, stuff that can be traded between countries. These are mostly physical goods like cars and coal and lumber. However, it has little effect on the nontradeable sector, things like retail and education. So if globalization has hurt the wages of American workers, you’d expect to see more downward pressure on wages in the tradeable sector than in the nontradeable sector.
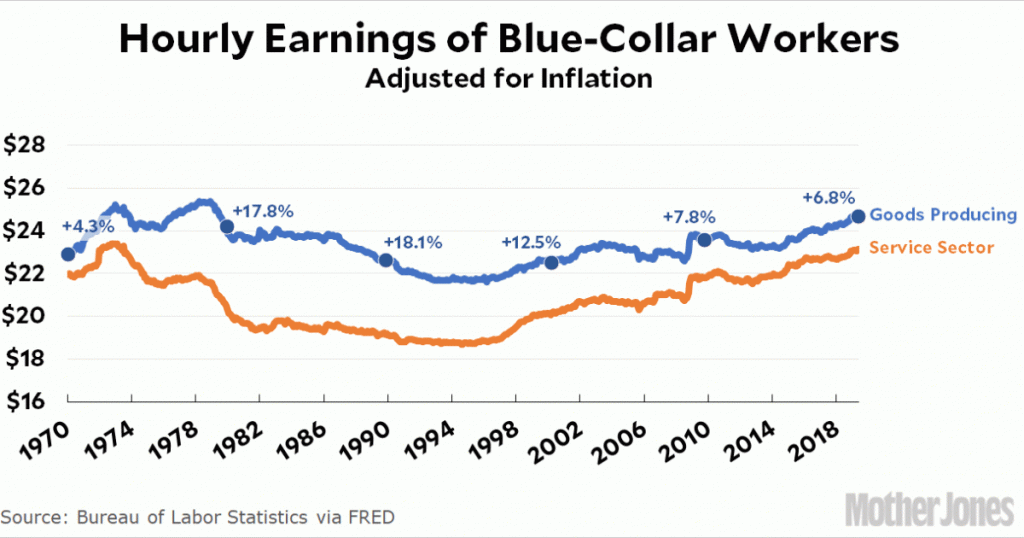
As a rough cut on this, you can look at blue-collar wages for goods-producing industries vs. service sector industries. Here it is:
In 1970, before the big wave of globalization hit, wages in goods-producing industries were 4 percent higher than in the service sector. Then, starting in 1980, when globalization began to take off, the service sector took a steep and sustained dive. It eventually started to catch up, but by 2019 it still hadn’t: wages in the goods-producing industries were 7 percent higher than in the service sector.
Globalization may well have pushed wages down in the goods-producing industries. But if that’s the case, why were wages in the service sector pushed down even more? The answer is inconvenient for corporations and the rich, who like to shrug their shoulders and say that it’s a global world these days and, hey, what can you do? The answer they’re all afraid of is: labor unions. Service-sector wages have lagged because, even in the current anemic state of organized labor, goods-producing industries still have more of a labor presence than the service sector.
A whole host of problems—income inequality, sluggish wage growth, unaffordable housing, the power of Wall Street—are just symptoms of the fact that American workers don’t have the bargaining power to demand higher wages. Fix that, and a whole lot of other problems will magically get fixed at the same time.