That Recent Abortion Study Is . . . Maybe Not the Final Word
Do women who get abortions later regret their choice? Robin Abcarian writes in the LA Times today about a study that concludes otherwise:
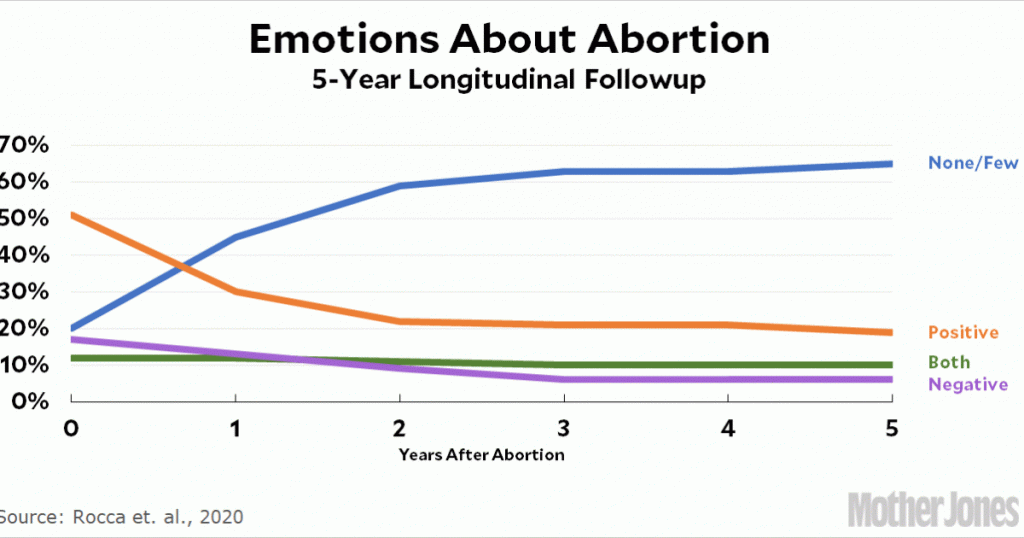
“Tons of studies have found that relief is the most common short-term emotion after abortion, despite mixed emotions,” said the paper’s lead author, UCSF epidemiologist Corinne Rocca. “But even after five years, when emotions are pretty low, relief is still the most common one.” She found that about 99% of women who had abortions told researchers five years later that they’d made the right decision.
….Some women, naturally, dropped out of the study over the five years, leading critics to suggest that these were women who felt regret, shame or guilt about having abortions. But Rocca closely analyzed who dropped out and did not find a correlation between dropouts and negative emotions. “People can make that claim,” she said, “but I didn’t find any of that.”
This is . . . not entirely honest. Of course people dropped out. People always drop out of longitudinal studies like this. The real criticism of Rocca’s study is that it included only women who agreed to participate in the first place.¹ In other words, her sample is self-selected, not random. She defends this:
38% enrollment for a five-year study asking women about a stigmatized health service is within the range of other large-scale prospective studies. Importantly, with the exception of being poorer, women in this sample were demographically similar to US women with unintended pregnancies. Also, women experienced a range of emotions at enrollment: approximately two-thirds expressed sadness and over one-third felt some regret. We have no reason to believe that women would select into the study based on how these emotions would evolve over three years.
It’s true that longitudinal studies, by definition, include only people who agree to be part of the study in the first place. If you’re studying some concrete physical phenomenon like lead poisoning or the effect of a new drug, that’s probably OK. But this is precisely why longitudinal studies aren’t generally useful for assessing things like emotional states, which can easily affect participation in unexpected ways. Rocca says “we have no reason to believe” that happened here, but that’s a pretty lackadaisical approach to legitimate criticism. I can think of half a dozen reasons off the top of my head why emotional states might affect participation. Maybe people who feel guilt are less likely to want to be reminded of it periodically for the next five years. Maybe introverts are less likely to participate. Maybe women with traditional upbringings are less likely to participate. Etc. This is an endless list, and “no reason to believe” mostly suggests that nobody bothered looking.
None of this means the study’s conclusions are wrong. My own guess, based on other research, is that it’s basically correct. That said, I just don’t see how you can claim to get any kind of reliable results from an extremely non-random sample like this. This is true both for studies we agree with and those we don’t.
¹It’s worth noting that this is true of survey-based studies too. This is just a fundamental problem when you’re studying something like emotional responses to abortion. Lots of people probably won’t want to participate, and it’s all but impossible to know for sure if that affects the randomness of your sample.